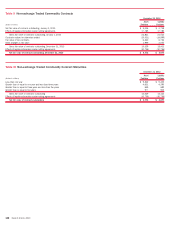
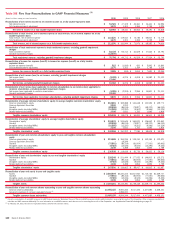
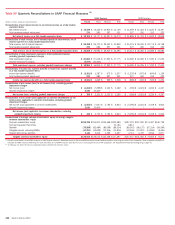
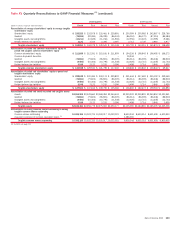
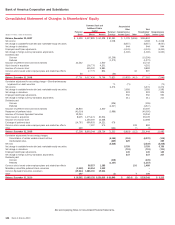
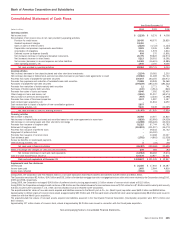
Bank of America 2010 Annual Report Download - page 138
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 138 of the 2010 Bank of America annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Glossary
Alt-A Mortgage – Alternative-A mortgage, a type of U.S. mortgage that, for
various reasons, is considered riskier than A-paper, or “prime,” and less risky
than “subprime,” the riskiest category. Alt-A interest rates, which are deter-
mined by credit risk, therefore tend to be between those of prime and subprime
home loans. Typically, Alt-A mortgages are characterized by borrowers with less
than full documentation, lower credit scores and higher LTVs.
Assets in Custody – Consist largely of custodial and non-discretionary trust
assets excluding brokerage assets administered for clients. Trust assets
encompass a broad range of asset types including real estate, private com-
pany ownership interest, personal property and investments.
Assets Under Management (AUM) – The total market value of assets under
the investment advisory and discretion of GWIM which generate asset man-
agement fees based on a percentage of the assets’ market values. AUM
reflects assets that are generally managed for institutional, high net-worth
and retail clients and are distributed through various investment products
including mutual funds, other commingled vehicles and separate accounts.
Bridge Financing – A loan or security that is expected to be replaced by
permanent financing (debt or equity securities, loan syndication or asset
sales) prior to the maturity date of the loan. Bridge loans may include an
unfunded commitment, as well as funded amounts, and are generally ex-
pected to be retired in one year or less.
Client Brokerage Assets – Include client assets which are held in brokerage
accounts. This includes non-discretionary brokerage and fee-based assets
which generate brokerage income and asset management fee revenue.
Client Deposits – Includes GWIM client deposit accounts representing both
consumer and commercial demand, regular savings, time, money market,
sweep and non-U.S. accounts.
Committed Credit Exposure – Includes any funded portion of a facility plus
the unfunded portion of a facility on which the lender is legally bound to
advance funds during a specified period under prescribed conditions.
Core Net Interest Income – Net interest income on a fully taxable-equivalent
basis excluding the impact of market-based activities.
Credit Card Accountability Responsibility and Disclosure Act of 2009
(CARD Act) – Legislation signed into law on May 22, 2009 to provide changes
to credit card industry practices including significantly restricting credit card
issuers’ ability to change interest rates and assess fees to reflect individual
consumer risk, change the way payments are applied and requiring changes
to consumer credit card disclosures. The majority of the provisions became
effective in February 2010.
Credit Default Swap (CDS) – A derivative contract that provides protection
against the deterioration of credit quality and allows one party to receive
payment in the event of default by a third party under a borrowing arrangement.
Excess Servicing Income – For certain assets that have been securitized,
interest income, fee revenue and recoveries in excess of interest paid to the
investors, gross credit losses and other trust expenses related to the secu-
ritized receivables are all classified as excess servicing income, which is a
component of card income. Excess servicing income also includes the
changes in fair value of the Corporation’s card-related retained interests.
Interest-only Strip – A residual interest in a securitization trust representing
the right to receive future net cash flows from securitized assets after
payments to third-party investors and net credit losses. These arise when
assets are transferred to a SPE as part of an asset securitization transaction
qualifying for sale treatment under GAAP.
Interest Rate Lock Commitment (IRLC) – Commitment with a loan applicant
in which the loan terms, including interest rate and price, are guaranteed for a
designated period of time subject to credit approval.
Letter of Credit – A document issued on behalf of a customer to a third party
promising to pay the third party upon presentation of specified documents. A
letter of credit effectively substitutes the issuer’s credit for that of the
customer.
Loan-to-value (LTV) – A commonly used credit quality metric that is reported in
terms of ending and average LTV. Ending LTV is calculated as the outstanding
carrying value of the loan at the end of the period divided by the estimated
value of the property securing the loan. Estimated property values are
primarily determined by utilizing the Case-Schiller Home Index, a widely used
index based on data from repeat sales of single family homes. Case-Schiller
indices are updated quarterly and are reported on a three-month or one-
quarter lag. An additional metric related to LTV is combined loan-to-value
(CLTV) which is similar to the LTV metric, yet combines the outstanding
balance on the residential mortgage loan and the outstanding carrying value
on the home equity loan or available line of credit, both of which are secured by
the same property, divided by the estimated value of the property. A LTV of
100 percent reflects a loan that is currently secured by a property valued at an
amount exactly equal to the carrying value or available line of the loan. Under
certain circumstances, estimated values can also be determined by utilizing
an automated valuation method (AVM) or Mortgage Risk Assessment Corpo-
ration (MRAC) index. An AVM is a tool that estimates the value of a property by
reference to large volumes of market data including sales of comparable
properties and price trends specific to the MSA in which the property being
valued is located. The MRAC index is similar to the Case-Schiller Home Index
in that it is an index that is based on data from repeat sales of single family
homes and is reported on a lag.
Making Home Affordable Program (MHA) – A U.S. Treasury program to
reduce the number of foreclosures and make it easier for homeowners to
refinance loans. The program is comprised of the Home Affordable Modifi-
cation Program (HAMP) which provides guidelines on loan modifications and is
designed to help at-risk homeowners avoid foreclosure by reducing monthly
mortgage payments and provides incentives to lenders to modify all eligible
loans that fall under the program guidelines and the Home Affordable Refi-
nance Program (HARP) which is available to homeowners who have a proven
payment history on an existing mortgage owned by FNMA or FHLMC and is
designed to help eligible homeowners refinance their mortgage loans to take
advantage of current lower mortgage rates or to refinance ARMs into more
stable fixed-rate mortgages. In addition, the Second Lien Program is a part of
the MHA. For more information on this program, see the separate definition
for the Second Lien Program.
Mortgage Servicing Right (MSR) – The right to service a mortgage loan when
the underlying loan is sold or securitized. Servicing includes collections for
principal, interest and escrow payments from borrowers and accounting for
and remitting principal and interest payments to investors.
Net Interest Yield – Net interest income divided by average total interest-
earning assets.
Nonperforming Loans and Leases – Includes loans and leases that have been
placed on nonaccrual status, including nonaccruing loans whose contractual
terms have been restructured in a manner that grants a concession to a
borrower experiencing financial difficulties (troubled debt restructurings or
TDRs). Loans accounted for under the fair value option, purchased credit-
impaired loans and loans held-for-sale are not reported as nonperforming
loans and leases. Consumer credit card loans, business card loans, con-
sumer loans not secured by real estate, and consumer loans secured by real
estate where repayments are insured by the Federal Housing Administration
are not placed on nonaccrual status and are, therefore, not reported as
nonperforming loans and leases.
Purchased Credit-impaired (PCI) Loan – A loan purchased as an individual
loan, in a portfolio of loans or in a business combination with evidence of
deterioration in credit quality since origination for which it is probable, upon
136 Bank of America 2010