Bank of America 2010 Annual Report Download - page 187
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 187 of the 2010 Bank of America annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Customer Vehicles
Customer vehicles include credit-linked and equity-linked note vehicles, repackaging vehicles and asset acquisition vehicles, which are typically created on
behalf of customers who wish to obtain market or credit exposure to a specific company or financial instrument.
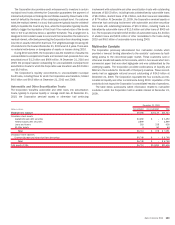
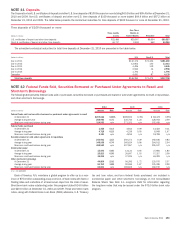
The table below summarizes select information related to customer vehicles in which the Corporation held a variable interest at December 31, 2010 and
2009.
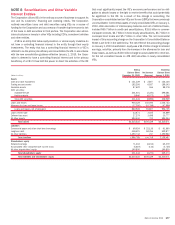
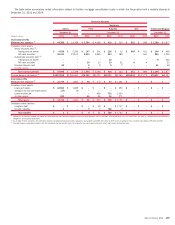
(Dollars in millions)
Consolidated Unconsolidated Total Consolidated Unconsolidated Total
2010 2009
December 31
Maximum loss exposure $4,449 $2,735 $ 7,184
$277 $10,229 $10,506
On-balance sheet assets
Trading account assets
$3,458 $ 876 $ 4,334
$183 $ 1,334 $ 1,517
Derivative assets
1 722 723
78 4,815 4,893
Loans and leases
–––
–6565
Loans held-for-sale
959 – 959
–––
All other assets
1,429 – 1,429
16 – 16
Total
$5,847 $1,598 $ 7,445
$277 $ 6,214 $ 6,491
On-balance sheet liabilities
Derivative liabilities
$1 $23$24
$ – $ 267 $ 267
Commercial paper and other short-term borrowings
–––
22 – 22
Long-term debt
3,457 – 3,457
50 74 124
All other liabilities
– 140 140
– 1,357 1,357
Total
$3,458 $ 163 $ 3,621
$ 72 $ 1,698 $ 1,770
Total assets of VIEs
$5,847 $6,090 $11,937
$277 $16,487 $16,764
Credit-linked and equity-linked note vehicles issue notes which pay a
return that is linked to the credit or equity risk of a specified company or
debt instrument. The vehicles purchase high-grade assets as collateral and
enter into credit default swaps or equity derivatives to synthetically create the
credit or equity risk to pay the specified return on the notes. The Corporation is
typically the counterparty for some or all of the credit and equity derivatives
and, to a lesser extent, it may invest in securities issued by the vehicles. The
Corporation may also enter into interest rate or foreign currency derivatives
with the vehicles. The Corporation also had approximately $338 million of
other liquidity commitments, including written put options and collateral value
guarantees, with unconsolidated credit-linked and equity-linked note vehicles
at December 31, 2010.
Repackaging vehicles issue notes that are designed to incorporate risk
characteristics desired by customers. The vehicles hold debt instruments
such as corporate bonds, convertible bonds or asset-backed securities with
the desired credit risk profile. The Corporation enters into derivatives with the
vehicles to change the interest rate or foreign currency profile of the debt
instruments. If a vehicle holds convertible bonds and the Corporation retains
the conversion option, the Corporation is deemed to have controlling financial
interest and consolidates the vehicle.
Asset acquisition vehicles acquire financial instruments, typically loans, at
the direction of a single customer and obtain funding through the issuance of
structured notes to the Corporation. At the time the vehicle acquires an asset,
the Corporation enters into total return swaps with the customer such that the
economic returns of the asset are passed through to the customer. The
Corporation is exposed to counterparty credit risk if the asset declines in value
and the customer defaults on its obligation to the Corporation under the total
return swaps. The Corporation’s risk may be mitigated by collateral or other
arrangements. The Corporation consolidates these vehicles because it has
the power to manage the assets in the vehicles and owns all of the structured
notes issued by the vehicles.
The Corporation’s maximum exposure to loss from customer vehicles
includes the notional amount of the credit or equity derivatives to which the
Corporation is a counterparty, net of losses previously recorded, and the
Corporation’s investment, if any, in securities issued by the vehicles. It has not
been reduced to reflect the benefit of offsetting swaps with the customers or
collateral arrangements.
Bank of America 2010 185