RBS 2009 Annual Report Download - page 122
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 122 of the 2009 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.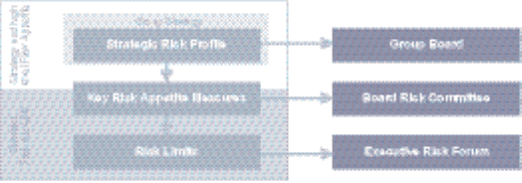
Business review continued
Risk, capital and liquidity governance* continued
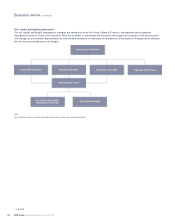
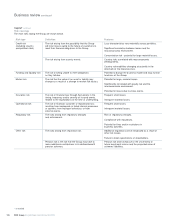
Management responsibilities
All employees have a role to play in the day-to-day management of
capital, liquidity and risk which is set and managed by specialist staff
in:
•Risk Management: credit risk, market risk, operational risk, regulatory
risk, reputational risk, insurance risk and country risk, together with
risk analytics; and
•Group Treasury: balance sheet, capital management, intra-group
exposure, funding, liquidity and hedging policies.
Independence underpins the approach to risk management, which is
reinforced throughout the Group by appropriate reporting lines. Risk
Management and Group Treasury functions are independent of the
revenue generating business. As part of the move towards greater
functional independence, the divisional Chief Risk Officers have a direct
reporting line to the Head of Restructuring and Risk as well as to their
divisional CEOs.
Group Internal Audit supports the GAC in providing an independent
assessment of the design, adequacy and effectiveness of the internal
controls relating to risk management.
Risk appetite
Risk appetite is an expression of the maximum level of risk that the
Group is prepared to accept in order to deliver its business objectives.
Risk and capital management across the Group is based on the risk
appetite set by the Board, who ultimately approve annual plans for each
division and regularly reviews and monitors the Group’s performance in
relation to risk.
Risk appetite is defined in both quantitative and qualitative terms as
follows:
•Quantitative: encompassing stress testing, risk concentration, VaR,
liquidity and credit related metrics; and
•Qualitative: ensuring that the Group applies the correct principles,
policies and procedures.
Different techniques are used to ensure that the Group’s risk appetite is
achieved. The Board Risk Committee considers and recommends for
approval by the Group Board, the Group’s risk appetite framework and
tolerance for current and future strategy, taking into account the Group’s
capital adequacy and the external risk environment. The ERF is
responsible for ensuring that the implementation of strategy and
operations are in line with the risk appetite determined by the Board.
This is reinforced through policy and limit frameworks ensuring that all
staff within the Group make appropriate risk and reward trade-offs
within pre-agreed boundaries.
The annual business planning and performance management
processes and associated activities together ensure that the expression
of risk appetite remains appropriate. Both GRC and GALCO support this
work.
* unaudited
Remuneration responsibilities
In August 2009, the Financial Services Authority (FSA) published its
Code of Remuneration Practices (the Code). The Code requires the
Group to establish, implement and maintain remuneration policies,
procedures and practices that promote and are consistent with effective
risk management.
The Risk Management function provides input to the Remuneration
Committee on the remuneration policy for the Group. Each division is
allocated risk objectives as part of the strategic plan and achievement
of these objectives is evaluated as part of the annual performance
management process.
During 2009 Risk Management provided formal independent 360°
feedback for key individuals, reviewing their capability and performance
in relation to managing risk. Individuals selected perform roles of
significant influence and their activities have, or could have, a material
impact on the Group’s risk profile.
An annual report on the risk performance of each division, including
both qualitative and quantitative information is provided to the
Remuneration Committee to allow consideration of adjustments relating
to the compensation for the performance year.
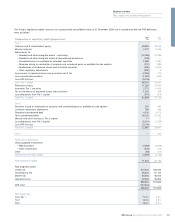
Capital*
Capital resources
It is the Group’s policy to maintain a strong capital base and to utilise it
efficiently throughout its activities to optimise the return to shareholders,
while maintaining a prudent relationship between the capital base and
the underlying risks of the business. In carrying out this policy, the
Group has regard to the supervisory requirements of the FSA. The FSA
uses Risk Asset Ratio (RAR) as a measure of capital adequacy in the
UK banking sector, comparing a bank’s capital resources with its risk-
weighted assets (RWAs) (the assets and off-balance sheet exposures
are ‘weighted’ to reflect the inherent credit and other risks); by
international agreement, the RAR should be not less than 8% with a
Tier 1 component of not less than 4%. At 31 December 2009, the
Group’s total RAR was 16.1% (2008 – 14.1%) and the Tier 1 RAR was
14.1% (2008 – 10.0%).
As part of the annual planning and budgeting cycle, each division is
allocated capital based upon RWAs and associated regulatory
deductions. The budgeting process considers risk appetite, available
capital resources, stress testing results and business strategy. The
budget is agreed by the Board and allocated to divisions to manage
their allocated RWAs.
Group Treasury and GALCO monitor available capital and its utilisation
across divisions. GALCO makes the necessary decisions around re-
allocation of budget and changes in RWA allocations.
RBS Group Annual Report and Accounts 2009120