RBS 2009 Annual Report Download - page 385
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 385 of the 2009 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
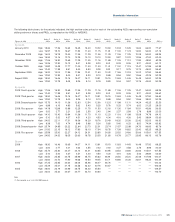
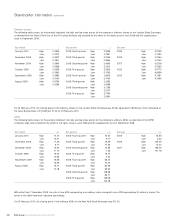
Shareholder information
383RBS Group Annual Report and Accounts 2009
Glossary of terms
Adjustable rate mortgage (ARM) – in the US a variable-rate mortgage.
ARMs include: hybrid ARMs which typically have a fixed-rate period
followed by an adjustable-rate period; interest-only ARMs where interest
only is payable for a specified number of years, typically for three to ten
years; and payment-option ARMs that allow the borrower to choose
periodically between various payment options.
Alt-A (Alternative A-paper) are mortgage loans with a higher credit
quality than sub-prime loans but with features that disqualify the
borrower from a traditional prime loan. Alt-A lending characteristics
include limited documentation; high loan-to-value ratio; secured on non-
owner occupied properties; and debt-to-income ratio above normal
limits.
Arrears are the aggregate of contractual payments due on a debt that
have not been met by the borrower. A loan or other financial asset is
said to be ’in arrears’ when payments have not been made.
Asset-backed commercial paper (ABCP) – a form of asset-backed
security generally issued by a commercial paper conduit.
Asset-backed securities (ABS) are securities that represent interests in
specific portfolios of assets. They are issued by a special purpose entity
following a securitisation. The underlying portfolios commonly comprise
residential or commercial mortgages but can include any class of asset
that yields predictable cash flows. Payments on the securities depend
primarily on the cash flows generated by the assets in the underlying
pool and other rights designed to assure timely payment, such as
guarantees or other credit enhancements. Collateralised bond
obligations, collateralised debt obligations, collateralised loan
obligations, commercial mortgage backed securities and residential
mortgage backed securities are all types of ABS.
Assets under management are assets managed by the Group on behalf
of clients.
Collateralised bond obligations (CBOs) are asset-backed securities for
which the underlying asset portfolios are bonds, some of which may be
sub-investment grade.
Collateralised debt obligations (CDOs) are asset-backed securities for
which the underlying asset portfolios are debt obligations: either bonds
(collateralised bond obligations) or loans (collateralised loan obligations)
or both. The credit exposure underlying synthetic CDOs derives from
credit default swaps. The CDOs issued by an individual vehicle are
usually divided in different tranches: senior tranches (rated AAA),
mezzanine tranches (AA to BB), and equity tranches (unrated). Losses
are borne first by the equity securities, next by the junior securities, and
finally by the senior securities; junior tranches offer higher coupons
(interest payments) to compensate for their increased risk.
Collateralised debt obligation squared (CDO-squared) is a type of
collateralised debt obligation where the underlying asset portfolio
includes tranches of other CDOs.
Collateralised loan obligations (CLOs) are asset-backed securities for
which the underlying asset portfolios are loans, often leveraged loans.
Collectively assessed loan impairment provisions – impairment loss
provisions in respect of impaired loans, such as credit cards or
personal loans, that are below individual assessment thresholds. Such
provisions are established on a portfolio basis, taking account the level
of arrears, security, past loss experience, credit scores and defaults
based on portfolio trends.
Commercial mortgage backed securities (CMBS) are asset-backed
securities for which the underlying asset portfolios are loans secured on
commercial real estate.
Commercial paper (CP) comprises unsecured obligations issued by a
corporate or a bank directly or secured obligations (asset-backed CP),
often issued through a commercial paper conduit, to fund working
capital. Maturities typically range from two to 270 days. However, the
depth and reliability of some CP markets means that issuers can
repeatedly roll over CP issuance and effectively achieve longer term
funding. Commercial paper is issued in a wide range of denominations
and can be either discounted or interest-bearing.
Commercial paper conduit is a special purpose entity that issues
commercial paper and uses the proceeds to purchase or fund a pool of
assets. The commercial paper is secured on the assets and is
redeemed either by further commercial paper issuance, repayment of
assets or liquidity drawings.
Commercial real estate – freehold and leasehold properties used for
business activities. Commercial real estate includes office buildings,
industrial property, medical centres, hotels, retail stores, shopping
centres, agricultural land and buildings, warehouses, garages etc.
Constant proportion portfolio insurance notes (CPPI notes) –CPPI is the
name given to a trading strategy that is designed to ensure that a fixed
minimum return is achieved either at all times or more typically, at a set
date in the future. Essentially the strategy involves continuously re-
balancing the portfolio of investments during the term of the product
between performance assets and safe assets using a pre-set formula.
CPPI notes provide investors with a return linked to a CPPI portfolio.
Contractual maturity is the date in the terms of a financial instrument on
which the last payment or receipt under the contract is due for
settlement.
Core Tier 1 capital – called-up share capital and eligible reserves plus
equity non-controlling interests, less intangible assets and other
regulatory deductions.
Core Tier 1 capital ratio – core Tier 1 capital as a percentage of risk-
weighted assets.
Cost:income ratio – operating expenses as a percentage of total income.
Covered mortgage bonds are debt securities backed by a portfolio of
mortgages that is segregated from the issuer’s other assets solely for
the benefit of the holders of the covered bonds.
Credit default swap (CDS) is a contract where the protection seller
receives premium or interest-related payments in return for contracting
to make payments to the protection buyer upon a defined credit event in
relation to a reference financial asset or portfolio of financial assets.
Credit events usually include bankruptcy, payment default and rating
downgrades.