RBS 2009 Annual Report Download - page 129
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 129 of the 2009 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Business review
Risk, capital and liquidity management
Credit risk
Credit risk is the risk arising from the possibility that the Group will incur
losses owing to the failure of customers to meet their financial
obligations. The quantum and nature of credit risk assumed in the
Group’s different businesses varies considerably, while the overall credit
risk outcome usually exhibits a high degree of correlation to the
macroeconomic environment. Certain disclosures in this section (pages
127 to 148) are unaudited and are labelled with an asterisk (*).
Principles for credit risk management
The key principles for credit risk management in the Group are as follows:
•A credit risk assessment of the customer and credit facilities is
undertaken prior to approval of credit exposure. Typically, this
includes both quantitative and qualitative elements including: the
purpose of the credit and sources of repayment; compliance with
affordability tests; repayment history; ability to repay; sensitivity to
economic and market developments; and risk-adjusted return based
on credit risk measures appropriate to the customer and facility type;
•Credit risk authority is specifically granted in writing to individuals
involved in the approval of credit extensions. In exercising credit
authority, individuals are required to act independently of business
considerations and must declare any conflicts of interest;
•Credit exposures, once approved, are monitored, managed and
reviewed periodically against approved limits. Lower quality
exposures are subject to more frequent analysis and assessment;
•Credit risk management works with business functions on the ongoing
management of the credit portfolio, including decisions on mitigating
actions taken against individual exposures or broader portfolios;
•Customers with emerging credit problems are identified early and
classified accordingly. Remedial actions are implemented promptly
and are intended to restore the customer to a satisfactory status and
minimise any potential loss to the Group; and
•Stress testing of portfolios is undertaken to assess the potential credit
impact of non-systemic scenarios and wider macroeconomic events
on the Group’s income and capital.
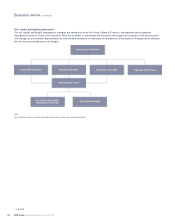
Credit risk organisation
The credit risk function is organised within a divisionally aligned
structure to ensure appropriate proximity to the businesses it covers and
to develop and provide the specialisation required to manage the
associated credit risk. The function comprises a number of activities:
credit approval; transaction/customer assessment; policy formulation
and development (in the context of the Group-wide policy framework);
portfolio reporting; and quantitative portfolio analytics.
In addition to the activities undertaken within divisional functions, a
Group-wide credit risk function sets the overall framework and highest
level credit risk policy standards; produces Group-wide credit risk
portfolio reporting and analysis; and approves credit transactions which
exceed divisional credit authority.
The Group Risk Committee (GRC) considers detailed reports of credit
risk performance such as monthly risk portfolio performance trend
information. The Group Credit Risk Policy Committee, a subcommittee of
the GRC, approves material new credit risk policy standards.
For wholesale credit portfolios, an updated Group-wide credit approval
and authority framework was introduced in early 2009, replacing the
previous structure of credit committees. The authority held by an
individual in respect of a particular extension of credit is determined by
a Group-wide credit approval grid which links total credit limit amount
for a customer group with customer credit quality (expressed as a credit
grade) and the individual’s credit experience and expertise (which
determines the authority level assigned to them). The Executive Credit
Group (ECG) considers credit decisions which exceed the delegated
authorities of individuals throughout the Group.
Global Restructuring Group (GRG)
GRG manages problem and potential problem exposures in the Group’s
wholesale credit portfolios. Its primary function is to work closely with the
Group’s customer facing businesses to support the proactive
management of any problem lending. This may include assisting with the
restructuring of a customer’s business and/or renegotiation of credit.
GRG reports to the Head of Restructuring and Risk and is structured
with specialist teams focused on: large corporate cases (higher value,
multiple lenders); small and medium size business cases (lower value,
bilateral relationships); and recovery/litigations.
Originating business units liaise with GRG upon the emergence of a
potentially negative event or trend that may impact a borrower’s ability to
service its debt. This may be a significant deterioration in some aspect
of the borrower’s activity, such as trading, where a breach of covenant
is likely or where a borrower has missed or is expected to miss a
material contractual payment to the Group or another creditor.
On transfer of a relationship to GRG a strategy is devised to:
•Work with the borrower to facilitate changes that will maximise the
potential for turnaround of their situation and return them to
profitability;
•Define the Group’s role in the turnaround situation and assess the
risk/return dimension of the Group’s participation;
•Return customers to the originating business unit in a sound and
stable condition or, if such recovery cannot be achieved, avoid
additional losses and maximise recoveries; and
•Ensure key lessons learned are fed back into origination policies and
procedures.
Retail collections and recoveries
There are collections and recoveries functions in each of the consumer
businesses. Their role is to provide support and assistance to
customers who are currently experiencing difficulties meeting their
financial obligations. Where possible, the aim of the collections and
recoveries teams is to return the customer to a satisfactory position, by
working with them to restructure their finances. If this is not possible, the
team has the objective of reducing the loss to the Group.
The ongoing investment in collections and recoveries operations has
continued in 2009. Investment has increased staffing levels in all
collections and recoveries functions, enhanced staff training to improve
efficiency and effectiveness as well as upgraded technology and
infrastructure.
127RBS Group Annual Report and Accounts 2009