RBS 2009 Annual Report Download - page 171
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 171 of the 2009 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285 -
 286
286 -
 287
287 -
 288
288 -
 289
289 -
 290
290 -
 291
291 -
 292
292 -
 293
293 -
 294
294 -
 295
295 -
 296
296 -
 297
297 -
 298
298 -
 299
299 -
 300
300 -
 301
301 -
 302
302 -
 303
303 -
 304
304 -
 305
305 -
 306
306 -
 307
307 -
 308
308 -
 309
309 -
 310
310 -
 311
311 -
 312
312 -
 313
313 -
 314
314 -
 315
315 -
 316
316 -
 317
317 -
 318
318 -
 319
319 -
 320
320 -
 321
321 -
 322
322 -
 323
323 -
 324
324 -
 325
325 -
 326
326 -
 327
327 -
 328
328 -
 329
329 -
 330
330 -
 331
331 -
 332
332 -
 333
333 -
 334
334 -
 335
335 -
 336
336 -
 337
337 -
 338
338 -
 339
339 -
 340
340 -
 341
341 -
 342
342 -
 343
343 -
 344
344 -
 345
345 -
 346
346 -
 347
347 -
 348
348 -
 349
349 -
 350
350 -
 351
351 -
 352
352 -
 353
353 -
 354
354 -
 355
355 -
 356
356 -
 357
357 -
 358
358 -
 359
359 -
 360
360 -
 361
361 -
 362
362 -
 363
363 -
 364
364 -
 365
365 -
 366
366 -
 367
367 -
 368
368 -
 369
369 -
 370
370 -
 371
371 -
 372
372 -
 373
373 -
 374
374 -
 375
375 -
 376
376 -
 377
377 -
 378
378 -
 379
379 -
 380
380 -
 381
381 -
 382
382 -
 383
383 -
 384
384 -
 385
385 -
 386
386 -
 387
387 -
 388
388 -
 389
389 -
 390
390
 |
 |

Business review
Risk, capital and liquidity management
169RBS Group Annual Report and Accounts 2009
Insurance risk*
All the disclosures in this section are unaudited and indicated with an
asterisk (*). The Group is exposed to insurance risk directly through its
general insurance and life insurance businesses.
Insurance risk arises through fluctuations in the timing, frequency and/or
severity of insured events, relative to the expectations at the time of
underwriting. Insurance risk is managed in four distinct ways:
•Underwriting and pricing risk management: is managed through the
use of underwriting guidelines which detail the class, nature and
type of business that may be accepted, pricing policies by product
line and brand and centralised control of wordings and any
subsequent changes;
•Claims risk management: is handled using a range of automated
controls and manual processes;
•Reserving risk management: is applied to ensure that sufficient funds
have been retained to handle and pay claims as the amounts fall
due, both in relation to those claims which have already occurred or
will occur in future periods of insurance. Reserving risk is managed
through detailed analysis of historical and industry claims data and
robust control procedures around reserving models; and
•Reinsurance risk management: is used to protect against adverse
claims experience on business which exceeds internal risk appetite.
The Group uses various types of reinsurance to transfer risk that is
outside the Group’s risk appetite, including individual risk excess of
loss reinsurance, catastrophe excess of loss reinsurance and quota
share reinsurance.
Overall, insurance risk is predictable over time, given the large volumes
of data. However, uncertainty does exist, especially around predictions
such as the variations in weather for example. Risk is minimised through
the application of documented insurance risk policies, coupled with risk
governance frameworks and the purchase of reinsurance.
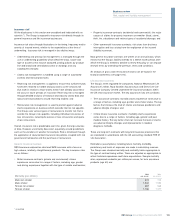
General insurance business
RBS Insurance underwrites retail and SME insurance with a focus on
high volume, relatively straightforward products. The key insurance risks
are as follows:
•Motor insurance contracts (private and commercial): claims
experience varies due to a range of factors, including age, gender
and driving experience together with the type of vehicle and location;
•Property insurance contracts (residential and commercial): the major
causes of claims for property insurance are weather (flood, storm),
theft, fire, subsidence and various types of accidental damage; and
•Other commercial insurance contracts: risk arises from business
interruption and loss arising from the negligence of the insured
(liability insurance).
Most general insurance contracts are written on an annual basis, which
means that the Group’s liability extends for a twelve month period, after
which the Group is entitled to decline to renew the policy or can impose
renewal terms by amending the premium, terms and conditions.
An analysis of gross and net insurance claims can be found in the
financial statements (see page 310).
Life assurance business
The Group’s three regulated life companies, National Westminster Life
Assurance Limited, Royal Scottish Assurance plc and Direct Line Life
Insurance Company Limited underwrite life insurance products within
the UK retail insurance market. The key assurance risks are as follows:
•Term assurance contracts: mortality claims experience varies due to
a range of factors, including age, gender and smoker status. The key
factors that increase the level of claims are disease pandemics and
adverse lifestyle changes; and
•Critical illness insurance contracts: morbidity claims experience
varies due to a range of factors, including age, gender and past
medical history. The key factors that can increase the level of claims
are adverse lifestyle changes and improvements in medical
diagnosis methods.
These are long-term contracts with long-term business provisions that
are calculated in accordance with the UK accounting standard FRS 27
‘Life Assurance’.
Estimations (assumptions) including future mortality, morbidity,
persistency and levels of expenses are made in calculating reserves.
The Group uses standard mortality and morbidity tables appropriate to
the type of contract being written. These are adjusted as appropriate to
reflect historical experience and future expectations. Sample mortality
rates, expressed as deaths per million per annum, for term assurance
products (age 40) are:
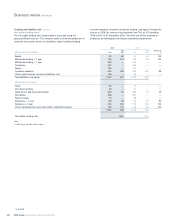
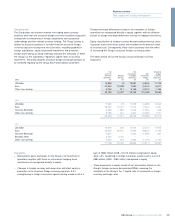
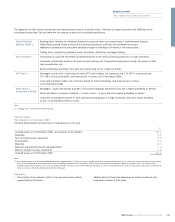
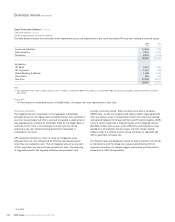
2009 2008
Mortality (per million) per annum per annum
Male non-smoker 674 723
Male smoker 1,542 1,590
Female non-smoker 497 568
Female smoker 1,136 1,277
* unaudited
