RBS 2010 Annual Report Download - page 148
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 148 of the 2010 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Risk management: Credit risk
All the disclosures in this section (pages 146 to 165) are audited unless
otherwise indicated by an asterisk (*).
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss owing to the failure of customers or
counterparties to meet payment obligations. The quantum and nature of
credit risk assumed across the Group's different businesses varies
considerably, while the overall credit risk outcome usually exhibits a high
degree of correlation to the macroeconomic environment.
Credit risk organisation
The existence of a strong credit risk management organisation is vital to
support the ongoing profitability of the Group. The potential for loss
through economic cycles is mitigated through the embedding of a robust
credit risk culture within the business units and through a focus on the
importance of sustainable lending practices. The role of the credit risk
management organisation is to own the credit approval, concentration
and risk appetite frameworks and to act as the ultimate authority for the
approval of credit. This, together with strong independent oversight and
challenge, enables the business to maintain a sound lending environment
within risk appetite.
Responsibility for development of Group-wide policies, credit risk
frameworks, Group-wide portfolio management and assessment of
provision adequacy sits within the functional Group Credit Risk
organisation (GCR) under the management of the Group Chief Credit
Officer. Execution of these policies and frameworks is the responsibility of
the risk management organisations located within the Group’s business
divisions. These divisional credit risk functions work together with GCR to
ensure that the Board’s expressed risk appetite is met within a clearly
defined and managed control environment. Each credit risk function
within the division is managed by a Chief Credit Officer who reports jointly
to a divisional Chief Risk Officer and to the Group Chief Credit Officer.
Divisional activities within credit risk include credit approval, transaction
and portfolio analysis, early problem recognition and ongoing credit risk
stewardship.
GCR is additionally responsible for verifying compliance by the divisions
with all Group credit policies. It is assisted in this by a credit quality
assurance function owned by the Group Chief Credit Officer and housed
within the divisions.
Credit risk appetite
Credit risk appetite is managed andcontrolled through a series of
frameworks designed to limit concentration by sector, counterparty,
country or asset class. These are supported by a suite of Group-wide and
divisional policies setting out the risk parameters within which business
units may operate. Information on the Group’s credit portfolios is reported
to the Board via the divisional and Group level risk committees detailed in
the Governance section on page 120.
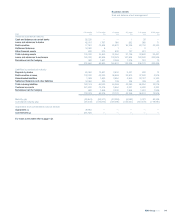
Product/asset class
xRetail: a formal risk appetite framework establishes Group-level
statements and thresholds that are cascaded through all retail
franchises in the Group and to granular business lines. These
include measures that relate to both aggregate portfolios and to
origination asset quality that are monitored frequently to ensure
consistency with Group standards and appetite. This appetite setting
and monitoring then informs the processes and parameters
employed in origination activities that require a large volume of small
scale credit decisions, typically involving an application for a new
product or a change in facilities on an existing product. The majority
of these decisions are based upon automated strategies utilising
credit and behaviour scoring techniques. Scores and strategies are
typically segmented by product, brand and other significant drivers
of credit risk. These data driven strategies utilise a wide range of
credit information relating to a customer including, where
appropriate, information across customers’ holdings. A small
number of credit decisions are subject to additional manual
underwriting by authorised approvers in specialist units. These
include higher value, more complex, small business and personal
unsecured transactions and some residential mortgage applications.
xWholesale: formal policies, specialised tools and expertise, tailored
monitoring and reporting and in certain cases specific limits and
thresholds are deployed to address certain lines of business across
the Group where the nature of credit risk incurred could represent a
concentration or a specific/heightened risk in some other form. Such
portfolios are subject to formal governance, including periodic review,
at either Group or divisional level, depending on materiality.
Sector
Across wholesale portfolios, exposures are assigned to, and reviewed in
the context of, a defined set of industry sectors. Through this sector
framework, appetite and portfolio strategies are agreed and set at
aggregate and more granular levels where exposures have the potential
to represent excessive concentration or where trends in both external
factors and internal portfolio performance give cause for concern. Formal
periodic reviews are undertaken at Group or divisional level depending on
materiality; these may include an assessment of the Group’s franchise in
aparticular sector, an analysis of the outlook (including downside
outcomes), identification of key vulnerabilities and stress/scenario tests.
Specific reporting on trends in sector risk and on status versus agreed
appetite and portfolio strategies is provided to senior management and to
the Board.
Single name
Within wholesale portfolios, much of the activity undertaken by the credit
risk function is organised around the assessment, approval and
management of the credit risk associated with a borrower or group of
related borrowers.
Aformal single name concentration framework addresses the risk of
outsized exposure to a borrower or borrower group. The framework
includes specific and elevated approval requirements; additional reporting
and monitoring; and the requirement to develop plans to address and
reduce excess exposures over an appropriate timeframe.
RBS Group 2010146
Business review continued