RBS 2010 Annual Report Download - page 196
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 196 of the 2010 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Risk management: Market risk continued
Risk measurement and control continued
The Global Market Risk Stress Testing Committee reviews and discusses
all matters relating to Market Risk Stress Testing. Stress test exposures
are discussed with senior management and relevant information is
reported to the Group Risk Committee, Executive Risk Forum and the
Board. Breaches in the Group’s market risk stress testing limits are
monitored and reported.
In addition to VaR and stress testing, the Group calculates a wide range
of sensitivity and position risk measures, for example interest rate ladders
or option revaluation matrices. These measures provide valuable
additional controls, often at individual desk or strategy level.
Model validation governance
Pricing models are developed and owned by the front office. Where
pricing models are used as the basis of books and records valuations,
they are all subject to independent review and sign-off. Models are
assessed by the Group Model Product Review Committee (GMPRC) as
having either immaterial or material model risk (valuation uncertainty
arising from choice of modelling assumptions), the assessment being
made on the basis of expert judgement. Those models assessed as
having material model risk are prioritised for independent quantitative
review. Independent quantitative review aims to quantify model risk (i.e.
the impact of missing risk factors in the front office model or the
possibility that we may be mismarking these products relative to other
market participants who may be using an alternative model) by
comparing model outputs against alternative independently developed
models. The results of the independent quantitative review are used by
Market Risk to inform risk limits and by Finance to inform reserves.
Governance over this process is provided by GMPRC, a forum which
brings together Front Office Quantitative Analysts, Market Risk, Finance
and Quantitative Research Centre (QuaRC), Group Risk’s independent
quantitative model review function.
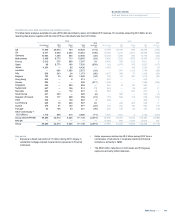
Risk (market risk, incremental default risk, counterparty credit risk)
models are developed both within business units and by Group functions.
Risk models are also subject to independent review and sign-off.
Meetings are held with the FSA every quarter to discuss the traded
market risk, including changes in models, management, back testing
results, risks not included in the VaR framework and other model
performance statistics.
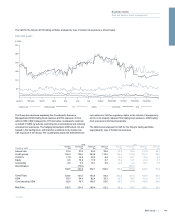
As part of the ongoing review and analysis of the suitability of the VaR
model, a methodology enhancement to the ABS VaR was approved and
incorporated into the regulatory model in 2010. The credit crisis in 2007 -
2009 caused large price changes for some structured bonds and the
spread based approach to calculating VaR for these instruments started
to give inaccurate risk levels, particularly for bonds trading at a significant
discount to par. The methodology enhancement harmonised the VaR
approach in the US and Europe by replacing the absolute spread-based
approach with a more reliable and granular relative price-based mapping
scheme. The enhancement better reflects the risk in the context of
position changes, downgrades and vintage as well as improving
differentiation between prime, Alt-A and sub-prime exposures.
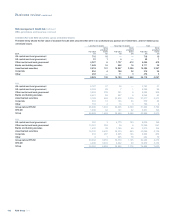
The VaR disclosure is broken down into trading and non-trading portfolios.
Trading VaR relates to the main trading activities of the Group and non-
trading reflects the risk associated with reclassified assets, money market
business and the management of internal funds flow within the Group’s
businesses.
Traded portfolios
The primary focus of the Group’s trading activities is to provide an
extensive range of debt and equity financing, risk management and
investment services to its customers, including major corporations and
financial institutions around the world. The Group undertakes these
activities organised along six principal business lines: money markets;
rates flow trading; currencies and commodities; equities; credit markets;
and portfolio management & origination.
Financial instruments held in the Group’s trading portfolios include, but
are not limited to: debt securities, loans, deposits, equities, securities sale
and repurchase agreements and derivative financial instruments (futures,
forwards, swaps and options).
The Group participates in exchange traded and over-the-counter (OTC)
derivatives markets. The Group buys and sells financial instruments that
are traded or cleared on an exchange, including interest rate swaps,
futures and options. Holders of exchange traded instruments provide
margin daily with cash or other security at the exchange, to which the
holders look for ultimate settlement.
The Group also buys and sells financial instruments that are traded OTC,
rather than on a recognised exchange. These instruments range from
commoditised transactions in derivative markets, to trades where the
specific terms are tailored to the requirements of the Group’s customers.
In many cases, industry standard documentation is used, most commonly
in the form of a master agreement, with individual transaction
confirmations.
Assets and liabilities in the trading book are measured at their fair value.
Fair value is the amount at which the instrument could be exchanged in a
current transaction between willing parties. The fair values are
determined following IAS 39 guidance which requires banks to use
quoted market prices or valuation techniques (models) that make the
maximum use of observable inputs. When marking to market using a
model, the valuation methodologies are reviewed and approved by the
market risk function. Group Risk provides an independent evaluation of
the model for transactions deemed by the Group Model Product Review
Committee (GMPRC) to be large, complex and/or innovative. Any profits
or losses on the revaluation of positions are recognised in the daily profit
and loss.
RBS Group 2010194
Business review continued