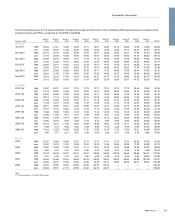
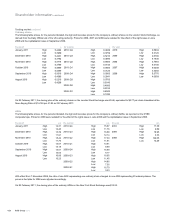
RBS 2010 Annual Report Download - page 437
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 437 of the 2010 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Covered mortgage bonds are debt securities backed by a portfolio of
mortgages that is segregated from the issuer's other assets solely for the
benefit of the holders of the covered bonds
Credit default swap (CDS) is a contract where the protection seller
receives premium or interest-related payments in return for contracting to
make payments to the protection buyer upon a defined credit event in
relation to a reference financial asset or portfolio of financial assets.
Credit events usually include bankruptcy, payment default and rating
downgrades.
Credit derivative product company (CDPC) is a special purpose entity
that sells credit protection under credit default swaps or certain approved
forms of insurance policies. Sometimes they can also buy credit
protection. CDPCs are similar to monoline insurers. However, unlike
monoline insurers, they are not regulated as insurers.
Credit derivatives are contractual agreements that provide protection
against a credit event on one or more reference entities or financial
assets. The nature of a credit event is established by the protection buyer
and protection seller at the inception of a transaction, and such events
include bankruptcy, insolvency or failure to meet payment obligations
when due. The buyer of the credit derivative pays a periodic fee in return
for a payment by the protection seller upon the occurrence, if any, of a
credit event. Credit derivatives include credit default swaps, total return
swaps and credit swap options.
Credit enhancements - are techniques that improve the credit standing of
financial obligations; generally those issued by an SPE in a securitisation.
External credit enhancements include financial guarantees and letters of
credit from third-party providers. Internal enhancements include excess
spread - the difference between the interest rate received on the
underlying portfolio and the coupon on the issued securities; and over-
collateralisation - on securitisation, the value of the underlying portfolio is
greater than the securities issued.
Credit risk assets -loans and advances (including overdraft facilities),
instalment credit, finance lease receivables and other traded instruments
across all customer types.
Credit risk spread - is the difference between the coupon on a debt
instrument and the benchmark or the risk-free interest rate for the
instrument's maturity structure. It is the premium over the risk-free rate
required by the market for the credit quality of an individual debt
instrument.
Credit valuation adjustments - are adjustments to the fair values of
derivative assets to reflect the creditworthiness of the counterparty.
Currency swap - an arrangement in which two parties exchange specific
principal amounts of different currencies at inception and subsequently
interest payments on the principal amounts. Often, one party will pay a
fixed interest rate, while the other will pay a floating exchange rate
(though there are also fixed-fixed and floating-floating arrangements). At
the maturity of the swap, the principal amounts are usually re-exchanged.
Customer accounts - comprise money deposited with the Group by
counterparties other than banks and classified as liabilities. They include
demand, savings and time deposits; securities sold under repurchase
agreements; and other short term deposits. Deposits received from banks
are classified as deposits by banks.
Debt restructuring - see Renegotiated loans.
Debt securities are transferable instruments creating or acknowledging
indebtedness. They include debentures, bonds, certificates of deposit,
notes and commercial paper. The holder of a debt security is typically
entitled to the payment of principal and interest, together with other
contractual rights under the terms of the issue, such as the right to
receive certain information. Debt securities are generally issued for a
fixed term and redeemable by the issuer at the end of that term. Debt
securities can be secured or unsecured.
Debt securities in issue comprise unsubordinated debt securities issued
by the Group. They include commercial paper, certificates of deposit,
bonds and medium-term notes.
Deferred tax asset -income taxes recoverable in future periods as a
result of deductible temporary differences - temporary differences
between the accounting and tax base of an asset or liability that will result
in tax deductible amounts in future periods - and the carry-forward of tax
losses and unused tax credits.
Deferred tax liability - income taxes payable in future periods as a result
of taxable temporary differences (temporary differences between the
accounting and tax base of an asset or liability that will result in taxable
amounts in future periods).
Defined benefit obligation - the present value of expected future
payments required to settle the obligations of a defined benefit plan
resulting from employee service.
Defined benefit plan - pension or other post-retirement benefit plan other
than a defined contribution plan.
Defined contribution plan - pension or other post-retirement benefit plan
where the employer's obligation is limited to its contributions to the fund.
Delinquency - a debt or other financial obligation is considered delinquent
when one or more contractual payments are overdue. Delinquency is
usually defined in terms of days past due. Delinquent and in arrears are
synonymous.
Deposits by banks - comprise money deposited with the Group by banks
and recorded as liabilities. They include money-market deposits,
securities sold under repurchase agreements, federal funds purchased
and other short term deposits. Deposits received from customers are
recorded as customer accounts.
Derivative - a contract or agreement whose value changes with changes
in an underlying index such as interest rates, foreign exchange rates,
share prices or indices and which requires no initial investment or an
initial investment that is smaller than would be required for other types of
contracts with a similar response to market factors. The principal types of
derivatives are: swaps, forwards, futures and options.
435RBS Group 2010
Shareholder information