RBS 2010 Annual Report Download - page 149
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 149 of the 2010 RBS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Credit approval authority is discharged by way of a framework of
individual delegated authorities that requires at least two individuals to
approve each credit decision, one from the business and one from the
credit risk management function. Both parties must hold sufficient
delegated authority under the Group-wide authority grid. Whilst both
parties are accountable for the quality of each decision taken, the credit
risk management approver holds ultimate sanctioning authority. The level
of authority granted to individuals is dependent on their experience and
expertise with only a small number of senior executives holding the
highest authority provided under the framework. Daily monitoring of
individual counterparty limits is undertaken.
At a minimum, credit relationships are reviewed and re-approved
annually. The renewal process addresses: borrower performance,
including reconfirmation or adjustment of risk parameter estimates; the
adequacy of security; and compliance with terms and conditions. For
certain counterparties, early warning indicators are also in place to detect
deteriorating trends of concern in limit utilisation or account performance.
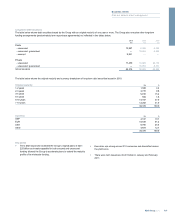
Single name concentrations
Reducing the risk arising from concentrations to single names remains a
key focus of management attention. Notwithstanding continued market
illiquidity and the impact of negative credit migration caused by the
current economic environment, significant progress was made in 2010
and credit exposures in excess of single name concentration limits fell by
over 40% during the year.
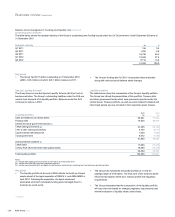
Country
Country risk arises from sovereign events (default or restructuring);
economic events (contagion of sovereign default to other parts of the
economy, cyclical economic shock); political events (convertibility
restrictions and expropriation or nationalisation); and natural disaster or
conflict. Such events have the potential to impact elements of the Group’s
credit portfolio that are directly or indirectly linked to the affected country
and can also give rise to market, liquidity, operational and franchise risk
related losses.
The framework for the Group’s appetite for country risk is set by the
Executive Risk Forum (ERF) in the form of limits by country risk grade,
with sub-limits on medium-term exposure. Authority is delegated to the
Group Country Risk Committee to manage exposures within the
framework, with escalation where needed to ERF. Specific limits are set
for individual countries based on a risk assessment taking into account
the Group’s franchise and business mix in that country. Additional
limitations (for example, on foreign-currency exposure and product types
with higher potential for loss in case of country events) may be
established to address specific vulnerabilities in the context of a country's
outlook and/or the Group's business strategy in a particular country. A
country watch list framework is in place to proactively monitor emerging
issues and facilitate the development of mitigation strategies.
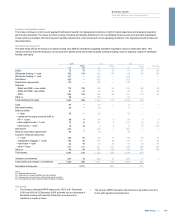
Global Restructuring Group
The Global Restructuring Group (GRG) manages problem and potential
problem exposures in the Group's wholesale credit portfolios. Its primary
function is to actively manage the exposures to minimise loss for the
Group and, where feasible, to return the exposure to the Group’s
mainstream loan book.
Originating business units consult with GRG prior to transfer to GRG
when a potentially negative event or trend emerges which might affect a
customer’s ability to service its debt or increase the Group’s risk
exposure to that customer. Such circumstances include deteriorating
trading performance, likely breach of covenant, challenging
macroeconomic conditions, a missed payment or the expectation of a
missed payment to the Group or another creditor.
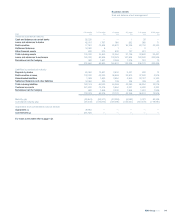
On transfer of the relationship, GRG devises a bespoke strategy that
optimises recoveries from the debt. This strategy may also involve GRG
reviewing the business operations and performance of the customer. A
number of alternative approaches will typically be considered including:
xCovenant relief:the temporary waiver or recalibration of covenants
may be granted to mitigate a potential or actual covenant breach.
Such relief is usually granted in exchange for fees, increased margin,
additional security, or a reduction in maturity profile of the original
loan.
xAmendment of restrictive covenants: restrictions in loan documents
may be amended or waived as part of an overall remedial strategy
to allow: additional indebtedness; the granting of collateral; the sale
of a business; the granting of junior lien on the collateral; or other
fundamental change in capital or operating structure of the
enterprise.
xVariation in margin: contractual margin may be amended to bolster
the customer’s day-to-day liquidity, with the aim of helping to sustain
the customer’s business as a going concern. This would normally be
accompanied by the Group receiving an exit payment, payment in
kind or deferred fee.
xPayment holidays and loan rescheduling: payment holidays or
changes to the contracted amortisation profile including extensions
in contracted maturity or roll-overs may be granted to improve
customer liquidity. Such concessions often depend on the
expectation that liquidity will recover when market conditions
improve or from capital raising initiatives that access alternative
sources of liquidity. Recently, these types of concessions have
become more common in commercial real estate transactions in
situations when a shortage of market liquidity rules out immediate
refinancing and short-term forced collateral sales unattractive.
xForgiveness of all or part of the outstanding debt: debt may be
forgiven or exchanged for equity where a fundamental shift in the
customer’s business or economic environment means that other
forms of restructuring strategies are unlikely to succeed in isolation
and the customer is incapable of servicing current debt obligations.
Debt forgiveness is often an element in leveraged finance
transactions which are typically structured on the basis of projected
cash flows from operational activities rather than underlying tangible
asset values. Maintaining the business as a going concern with a
sustainable level of debt is the preferred option rather than realising
the underlying assets, provided that the underlying business model
and strategy are considered viable.
147RBS Group 2010
Business review
Risk and balance sheet management